April is Testicular Cancer Awareness Month
It’s estimated that 9,910 men will be diagnosed with testicular cancer in 2022 in the U.S.
The incidence rate of testicular cancer has been increasing in the US and many other countries for several decades. The increase is mostly in seminomas. Experts have not been able to find reasons for this. Lately, the rate of increase has slowed.
Testicular cancer is not common: about 1 of every 250 males will develop testicular cancer at some point during their lifetime.
What is Testicular Cancer?
Testicular cancer occurs in the testicles (testes), which are located inside the scrotum, a loose bag of skin underneath the penis. The testicles produce male sex hormones and sperm for reproduction.
Many men who develop testicular cancer have no risk factors at all. However, certain conditions such as undescended testicle(s), HIV infection, abnormal testicular development and a family history of testicular cancer may increase the odds of developing testicular cancer.
Testicular Cancer Signs and Symptoms
The most common symptom associated with the disease is swelling or discomfort in the scrotum. However, men who experience any of the following symptoms are encouraged to speak with their health care provider:
A painless lump or swelling in either testicle
A dull ache in the lower abdomen or groin
Pain or discomfort in a testicle or the scrotum
A change in how the testicle feels
A sudden build-up of fluid in the scrotum
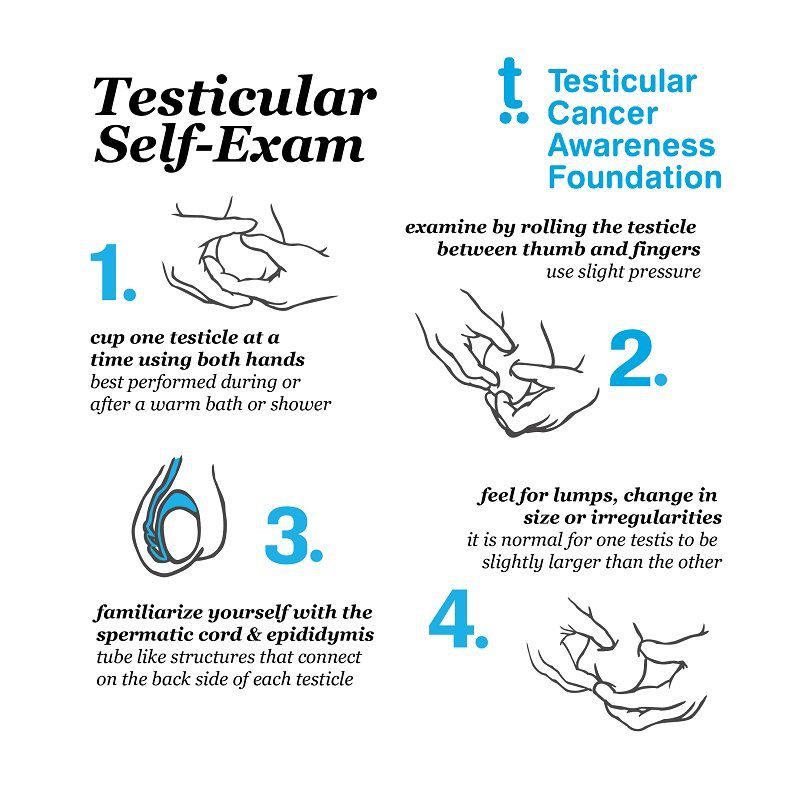
Monthly Testicular Self-Exams
Self-examination of the testes is important for early detection of testicular cancer. The most common method of early detection is performing a monthly exam. Since TC is usually isolated to a single testicle, comparison of your testicle with the other can be helpful. It is normal for one testicle to be slightly larger than the other. Your focus should be noticing any changes from the previous month.
Upon reaching puberty, all men should conduct a monthly testicular self-exam and ask your doctor during your yearly physical to perform one as well.
This is a COPYRIGHT image that belongs to TCAF. Please share, but do not modify or alter image in any way.

